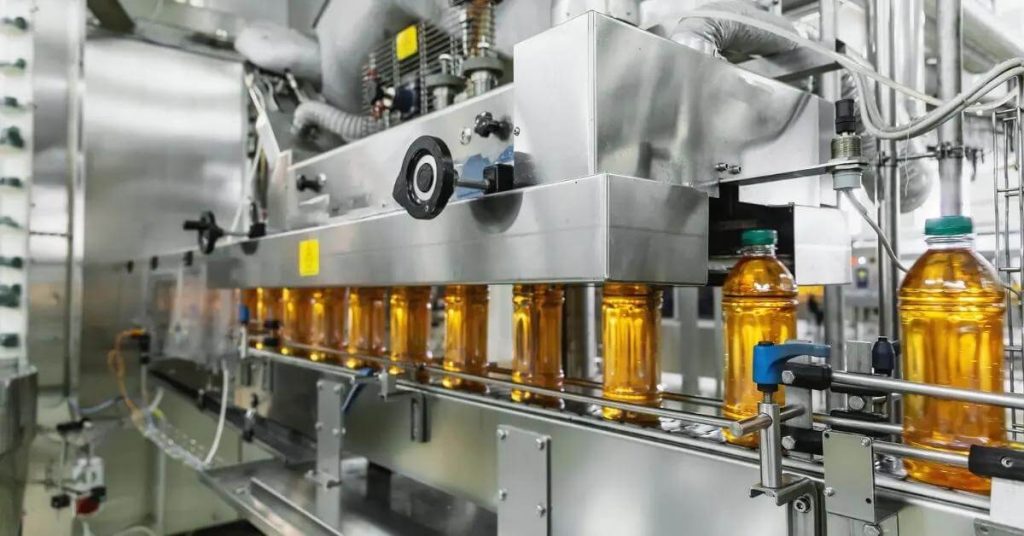
Ever thought about the journey your favorite beverage takes before it reaches you? Ever wondered why some drinks are shelf-stable, while others need refrigeration? That’s where the battle of hot filling vs cold filling beverages comes into play.
This may appear to be an insignificant point, yet for those in the beverage business – and anybody who appreciates a tasty sip of something – it’s a fundamental part of making safe, delightful drinks.
In this deep dive, we’ll explore hot filling vs cold filling beverages in detail. We’ll show you how each method works, which types of packaging they suit best and even take a quick look at alternative techniques such as aseptic filling.
Hot Filling in the Beverage Industry
The hot filling process is a tried-and-true method in the beverage industry, known for its effectiveness and reliability. By heating both the product and container to high temperatures, it eliminates harmful bacteria, ensuring safety and quality.
The Science Behind Hot Filling
In hot filling, beverages are heated between 194 and 203 degrees Fahrenheit—a temperature range carefully selected for maximum efficiency. This heat treatment, as approved by FDA guidelines, not only kills off any lurking pathogens but also helps preserve flavors without relying on artificial preservatives or additives.
A major player here is time—specifically High Temperature Short Time (HTST) processing. The HTST concept involves blasting food products with high heat over a short duration before quickly cooling them down again. In doing so, it safeguards flavor integrity while still killing off harmful microbes that can compromise product safety.
Common Applications of Hot Filling
This process isn’t just about eradicating potential health risks—it’s also about making sure your drink tastes great too. As such, acidic food products like vinegar-based sauces or sports drinks often undergo hot fill processes to maintain their punchy profiles longer than they might otherwise be able to do under normal circumstances.
Beverages packaged using this method include:
-
- Sodas: carbonation needs protection from microbial contamination during packaging.
-
- Vinegar-based Sauces: Vinegar’s naturally high acidity makes these sauces perfect candidates for hot-fill methods as this process enhances their shelf-life.
-
- Fruit Juices and Teas: Glass bottles filled with these beverages retain the freshness of taste post-processing thanks to the hot fill’s sterilization effects.
When it comes to packaging hot-filled products, the materials must withstand high temperatures to ensure quality and safety. Commonly used packaging materials for hot-filled items encompass:
-
Glass: Known for its excellent heat resistance, glass is a popular choice for hot-filling. It maintains the integrity of acidic foods and beverages without leaching chemicals.
-
Cardboard: Although less common, some food-grade, heat-resistant cardboard options exist. These are often used when combined with other protective materials.
-
Heat-resistant Plastics: Specialized plastics are engineered to endure the high temperatures of the hot-filling process. These plastics are sturdy and provide a lightweight alternative to glass.
Key Takeaway:
Hot filling is a trusted process in the beverage industry, using high heat to zap bacteria and maintain flavor quality.
It’s especially handy for acidic foods like vinegar-based sauces sports drinks, and even carbonated sodas. The goal? A safer, tastier drink that stays fresh longer.
Cold Filling In The Beverage Industry
Ever wondered why some beverages taste so fresh and authentic, almost as if they were just made? The secret often lies in the filling process. Specifically, cold filling.
The Process Behind Cold Filling
What exactly is the cold filling process? Basically, cold filling uses icy cold temperatures to kill bacteria lurking around in food packaging. But here’s what makes it unique – instead of heating things up as its counterpart hot fill method does, this procedure uses chilly conditions.
To get started with this cool technique, manufacturers first need to create an air purification room isolation zone where the actual filling happens. Picture something similar to a super clean lab from sci-fi movies; that’s how sterile we’re talking about.
Here’s where PET bottles enter into play. Known for their durability and versatility under various temperature ranges including extreme cold ones these are usually chosen as the container of choice during this process.
Why Cold Filling is Rising in Popularity
Cold filling has become more favored over hot filling for several compelling reasons:
-
Natural Ingredients: Unlike hot filling, which often relies on preservatives and additives to keep foods shelf-stable, cold filling can maintain the product’s freshness without these extra chemicals. This appeals to consumers who are actively seeking natural, clean-label products.
-
Preservation of Nutrients and Flavors: The cold filling process preserves the nutritional value and original taste of food products. Since there’s no heat involved, vitamins and subtle flavors remain intact, offering a superior eating experience.
-
Improved Product Quality: The absence of thermal processing means cold-filled products retain their texture and color. This results in a more appealing and high-quality product that aligns with consumer desires for visually and texturally engaging food.
-
Environmental Advantages: Cold filling can be more energy-efficient than traditional hot filling methods. By eliminating the need for extensive heating, companies can reduce energy consumption, aligning with sustainable practices and catering to eco-conscious consumers.
-
Extended Freshness: Despite the lack of preservatives, cold filling still effectively extends the product’s shelf life through advanced refrigeration technologies, providing a fresh option with the convenience consumers expect.
The trend towards cold filling is driven by a perfect storm of consumer preference for natural ingredients, high-quality products, environmental sustainability, and extended product freshness without compromising on safety.
Beverages Best Suited for Cold Filling
Which drinks best benefit from this ice-cold method? If your drink includes dairy ingredients or needs to remain cool throughout storage and transportation stages without any change in flavor profile or texture quality then cold filling is best.
FDA guidelines further state that products such as co-packed food items containing significant amounts of dairy components are also great candidates due to the higher safety standards required by such foods.
While cold filling may seem like the magical solution to all your beverage production needs, it’s not always suitable for every product out there. Certain factors like specific ingredients or desired shelf life can tip the scale towards hot fill methods instead.
Key Takeaway:
Shelf life and product ingredients can impact whether cold filling is the right choice. That’s why it’s crucial to consider every aspect of your drink, from its ingredients to its safety standards.
After all, you want to ensure that each sip delivers the freshness and flavor you intended.
What Is Aseptic Filling?
Aseptic filling in the beverage industry uses a technique that employs sterilization and packaging under sterile conditions to extend shelf life without preservatives or refrigeration. This is used for particularly high-acid products.
So how does this process work? It’s all about creating an aseptic environment. The product, container, and closures are first sterilized separately using steam or peracetic acid – a potent antimicrobial agent used widely in the pharmaceutical industry.
The next step involves transferring these components into an air purification room isolation area. Here icy cold air blasts through to ensure absolute sterility before filling begins. Any potential contaminants lurking around are swiftly dealt with.
This method has seen wide application across food products including juice which needs to remain fresh while also having extended shelf-life properties.
The Benefits of Aseptic Filling
If you’ve got your sights set on conquering foreign markets with your beverage line-up, consider this: a product processed via the aseptic method can last up to 18 months. That’s right; it offers fantastic durability when compared with other methods such as hot fill or cold fill processes that might not give similar longevity results.
Besides longevity benefits, there’s another major plus point associated with the use of specific ingredients during the production phase—preservation of nutritional value.
High temperature short time (HTST) treatment involved in hot filling may cause loss of nutrients whereas extremely low temperatures used in cold fill techniques might not be suitable for certain types of beverages due to its effect on consistency and texture. According to FDA guidelines, manufacturers must provide accurate information regarding nutritional content on their labels, and using aseptic filling can help ensure this accuracy.
Should You Use Aseptic Filling?
Apart from being an effective method to maintain the freshness of your beverages, it also caters well to modern consumer demands. People today prefer fresh products including juice that have extended shelf-life without artificial food additives or preservatives – exactly what aseptic filling provides.
Key Takeaway:
Aseptic filling offers longer shelf life and minimal preservatives. Aseptic filling truly revolutionizes the way we approach beverage production, marrying advanced technology with consumer needs for healthier, fresher options.
Hot Filling vs Cold Filling: A Comparative Analysis
In the beverage industry, hot and cold fill methods are two of the most popular approaches. But each one has its unique pros and cons.
Comparing Sterilization Processes
The hot filling process uses heat treatment to sterilize both the product and its container during food packaging. The food or drink is heated between 194-203 degrees Fahrenheit – this high-temperature short-time method effectively kills bacteria ensuring safe consumption.
In contrast, cold filling employs extreme cold as a weapon against harmful microbes in food packaging. This icy blast creates an environment that’s unfriendly to bacteria growth without changing the taste or texture of beverages like dairy drinks.
Product Quality and Shelf Life
Maintaining quality while extending shelf life is vital for any product on market shelves. The hot-fill process ensures excellent safety standards by killing potential contaminants with high heat. However, certain products may lose some natural flavors due to such intense temperatures.
The cold fill technique might help preserve those authentic tastes because it remains cool throughout; but let’s not forget about its downside: more preservatives may need to be added to ensure a longer shelf-life compared with hot-filled items.
This comparative analysis aims to give you insights into both these essential processes used in the beverage industry. You must consider what your specific needs are before deciding which method suits best for your product.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Hot Filling and Cold Filling
Choosing the right filling process for your beverage is a key decision. It’s not just about which technique is the most efficient in a laboratory setting, but also how it can affect flavor, storage life, and costs. So let’s break down some factors you should consider when deciding between hot filling or cold filling.
The Nature of Your Beverage
The first thing to think about is your product type. Some beverages are better suited for hot filling like isotonic drinks or those with specific ingredients that can withstand high temperature short time exposure without losing their flavor profile.
In contrast, fresh products including juice may need cold fill methods to keep them at their freshest. The icy cold air used in this method keeps these types of beverages tasting as they should – crisp and refreshing.
Sterilization Process
Both processes work on the principle of sterilizing both product and packaging container before sealing them off from any further contact with outside elements. But each does so differently.
The hot filling process blasts food packaging containers with heat up to 203 degrees Fahrenheit for a short period killing bacteria efficiently while ensuring quality remains intact.
Packaging Material Compatibility
Your choice might also be influenced by the type of packaging material you intend to use. Cold fill procedures often require PET bottles, since glass could shatter due to its inability to handle drastic changes in temperatures involved during this procedure. Glass bottles, however, are suitable for hot fill processes.
Remember, the ultimate goal is to protect food and beverages from contamination while maintaining taste. Deciding between hot filling and cold filling methods for your product requires a thorough understanding of it.
The Role of Ingredients in Choosing Filling Process
Ingredients play a significant role when it comes to choosing between hot filling and cold filling processes. The type, stability, and quality of the ingredients can directly impact the choice of method.
Beverage Formulation – Hot vs Cold Filling
In beverages that contain specific ingredients like dairy or certain proteins, preserving freshness becomes crucial. For such fresh products including juice and isotonic drinks, using an icy cold air process may be more beneficial. This is because these ingredients remain cool during the entire filling process.
On the other hand, for beverage formulations with higher acidity levels or those containing food additives needing sterilization for safety reasons, hot fill might be a better fit. It’s worth noting that this high temperature short time approach also ensures longevity without refrigeration which makes it perfect for non-perishable items.
Considering Ingredient Sensitivity
Certain delicate elements within your drink formulation might need extra care during packaging as well. Take probiotics in kombucha drinks as an example – they are heat-sensitive so they thrive better with aseptic cold filling methods in contrast to traditional hot fills.
Sensitivity towards peracetic acid used often in cleaning containers before any kind of fill is another point to consider while deciding upon your ideal procedure.
Impact on Flavor Profile
If you’ve ever noticed how canned soup tastes different from homemade ones then you’d know exactly what we’re talking about here. Hot-filled foods tend to have slightly altered taste profiles due to heating them at around 194-203 degrees Fahrenheit unlike cold-filled items.
So, if you are aiming for a certain flavor profile in your beverage product, it is worth considering the potential impact of the filling process on taste. It’s these small things that can make all the difference to consumers and ultimately determine how successful your product will be in the competitive food-beverage industry.
Key Takeaway:
In beverage manufacturing, Your filling choice depends heavily on the specific needs of your product. Factors like ingredients, freshness requirements, and acidity levels all come into play.
So whether you’re dealing with fresh juices that could benefit from a cool fill or high-acid drinks that need sterilization through a hot fill—each has its own best fit.
And let’s not forget about delicate elements such as probiotics—they demand extra care during packaging and might just flourish more under an aseptic cold fill process.
Hot Filling vs Cold Filling Beverages: Which Is Right For You?
The quality, safety, and longevity of your drink depend on your choice of hot filling or cold filling. Hot filling vs cold filling beverages require careful consideration.
The hot fill process uses high heat to sterilize both the product and its container, making it ideal for acidic drinks like sodas or sports juices. Cold fill leverages icy cold temperatures to kill bacteria without needing additives or preservatives – perfect for dairy-based products.
But remember: choosing between these two isn’t always black-and-white. The type of beverage you’re dealing with can sway this decision significantly.
If neither seems fitting, consider aseptic filling as an alternative that caters well to high-acid products while offering an extended shelf life of up to 18 months!
No matter which path you take in the beverage industry, keeping FDA regulations front of mind is crucially important.
When you’re ready, look to the beverage formulation and manufacturing experts – contact Meta Brand.